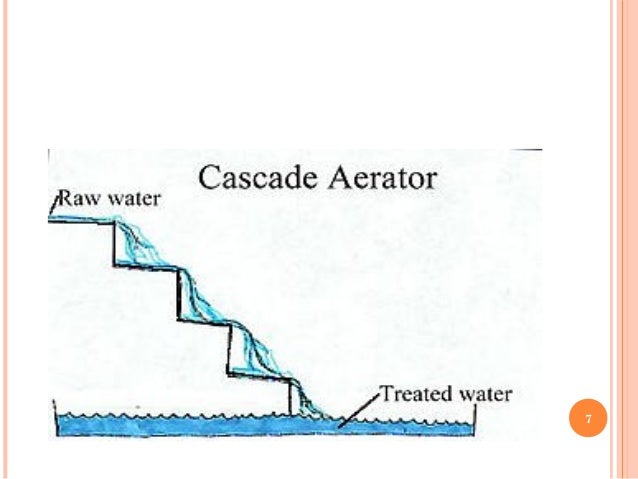
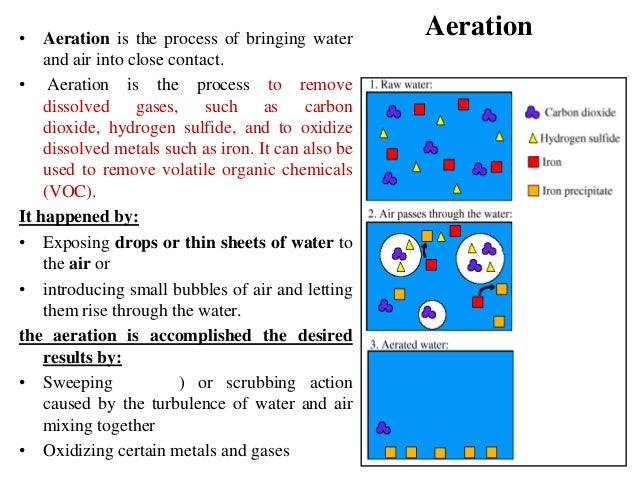
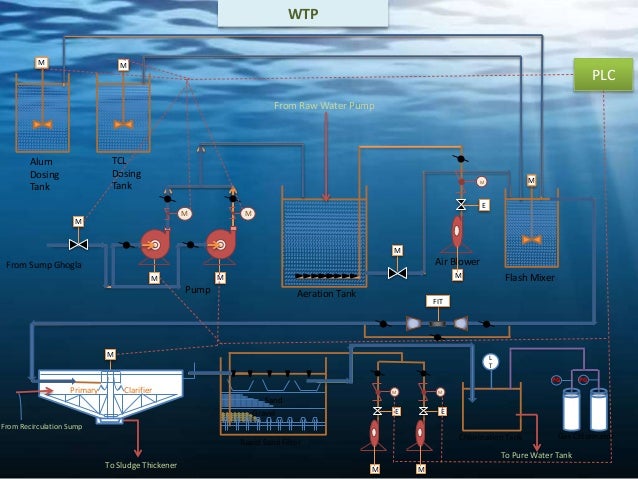
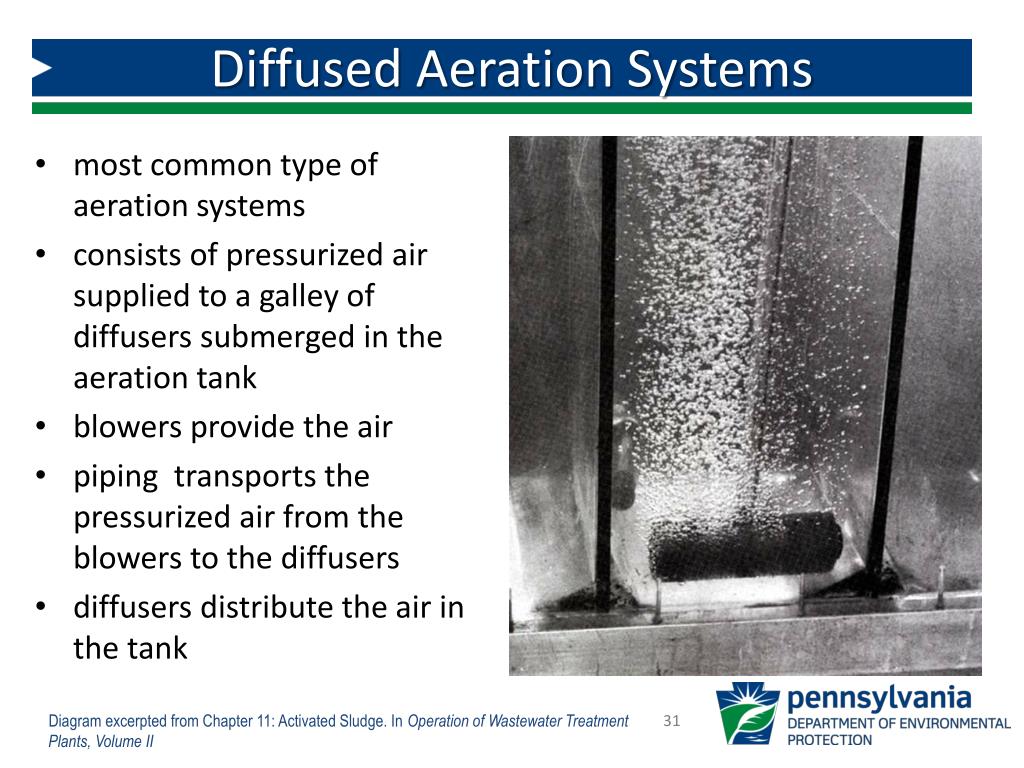
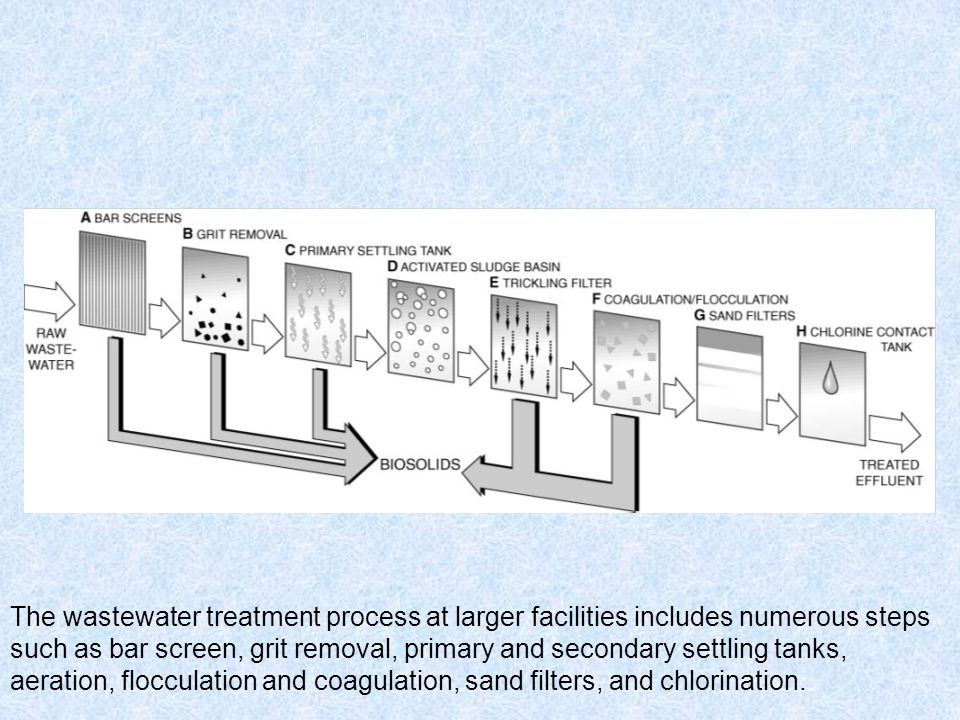
Water aeration is often required in water bodies that suffer from hypoxic or anoxic conditions often caused by upstream human activities such as sewage discharges agricultural run off or over baiting a fishing lake.
Aeration water treatment ppt.
Aeration is the process of bringing water and air into close contact in order to remove dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide and to oxidize dissolved metals such as iron.
Decrease co 2 concentration thereby reduce its corrosiveness.
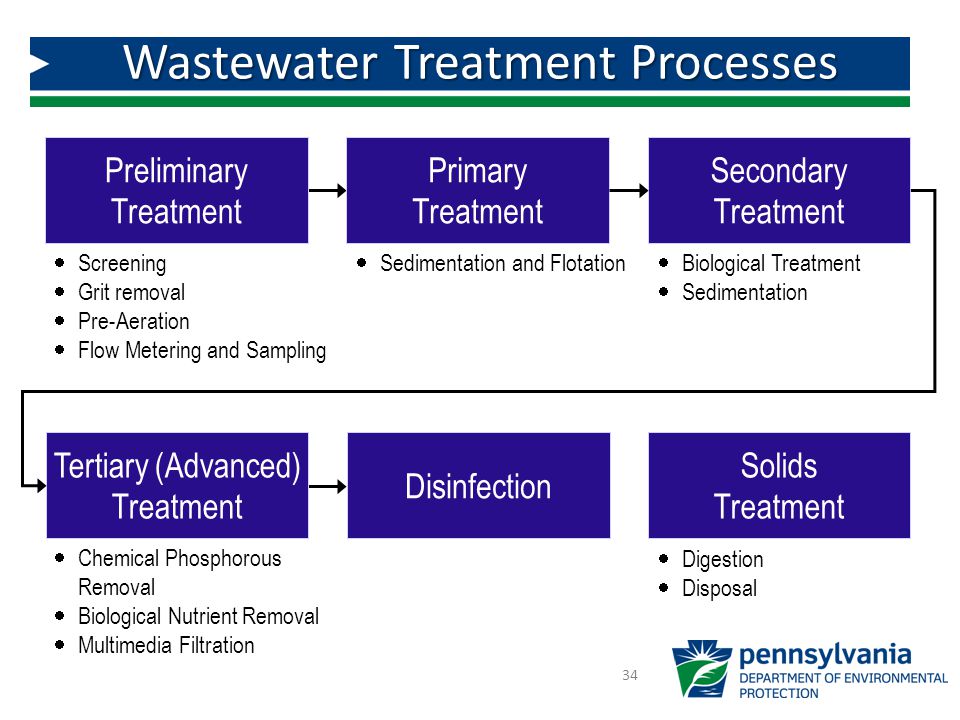
Wastewater treatment the effective treatment of wastewater to meet water quality objectives for water reuse applications and to protect public health is a critical.
Aeration is used for many purposes in water treatment the main uses are.
Aeration water treatment is effective for management of dissolved gases such as radon carbon dioxide some taste and odor problems such as methane and hydrogen sulfide as well as volatile organic compounds like mtbe or industrial solvents it is also effective in precipitating dissolved iron and manganese aeration raises the ph of water.
Aeration is often the first major process at the treatment plant.
A flocculant is defined as a substance which promotes the clumping of particles especially one used in treating waste water in order to improve the process the flocculant.
It can also be used to remove volatile organic chemicals voc in the water.
Carbon dioxide is produced as a result of the acid treatment and aeration is employed to rid the water of this corrosive gas.
An ample and evenly distributed oxygen supply in an aeration system is the key to rapid economically viable and effective wastewater treatment.
To remove tastes and odors caused by gases due to decomposition.
Aeration removal of dissolved gases degasification co 2 primary applications in water treatment high solubility of co 2reduces the ph ofwater which causes excessive consumption of lime or other neutralizing agents in coagulation and softening process the corrosiveness of water is also higher at lower ph values.
Aeration is often used to reduce the carbon dioxide liberated by a treatment process.
For example acid may be fed to the effluent of sodium zeolite softeners for boiler alkalinity control.
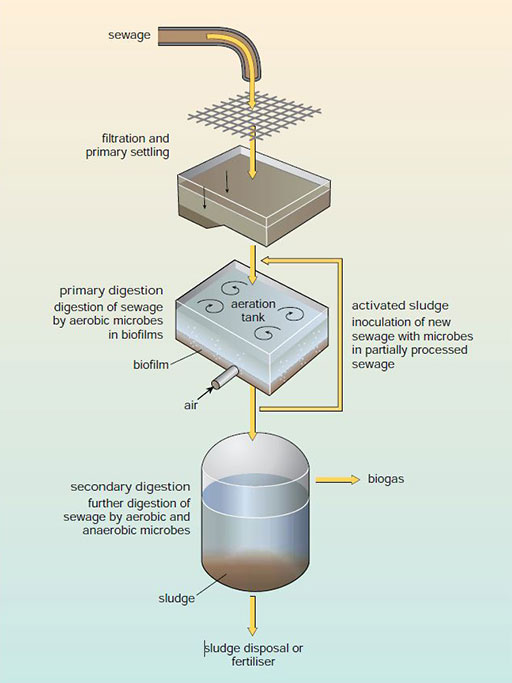
What you need to know about wastewater aeration and how it works views when wastewater is aerated enough its organic matter reduces and a flocculant sludge consisting of various microorganisms is formed.
Aeration is the most critical component of a treatment system using the activated sludge process.
Reduce taste and odor caused by dissolved gases such as hydrogen sulphide h 2 s and methane ch 4 that are removed during aeration.
It is the process of bringing water in intimate contact with air so as to absorb oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide gas.
Areation and types of aeration in waste water treatment 1.
To increase dissolved oxygen content.
A well designed aeration system has a direct impact on the level of wastewater treatment it achieves.